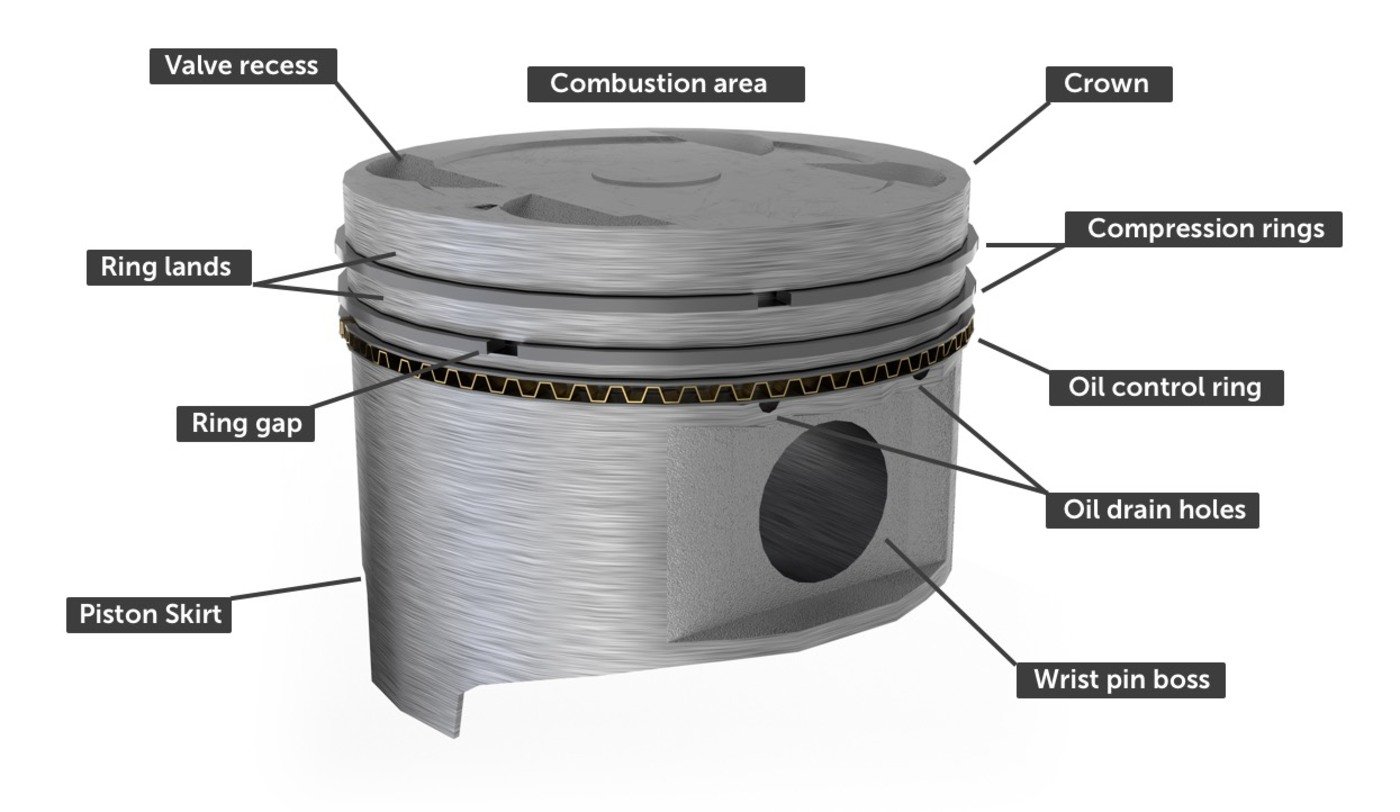
Pistons, the heart of an engine, are typically made of aluminum alloy. This material strikes a balance between strength and lightness, crucial for engine performance. The construction of pistons involves precision engineering to withstand high temperatures and pressures within the combustion chamber. Understanding what are pistons made of is key to appreciating their role in powering vehicles and machinery efficiently.
Exploring What Pistons are Made of
Introduction to Pistons
Pistons are a crucial component in internal combustion engines, playing a vital role in converting pressure into mechanical energy. Have you ever wondered what these essential engine parts are made of? Let’s delve into the world of pistons and explore the materials that make them sturdy and reliable.
Historical Evolution of Piston Materials
Over the years, piston materials have evolved significantly to meet the demanding requirements of modern engines. In the early days of automotive engineering, pistons were primarily made of cast iron due to its affordability and durability. However, advancements in material science have led to the development of a wide range of materials that offer improved performance and efficiency.
Common Materials Used in Piston Manufacturing
1. Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are the most commonly used materials in piston manufacturing today. These alloys offer a perfect balance of strength, lightweight, and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-performance engines. The most popular aluminum alloys used in pistons include 2618, 4032, and 6061.
2. Cast Iron
While less common in modern engines, cast iron pistons are still used in certain applications where high strength and wear resistance are essential. Cast iron pistons are known for their durability and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
3. Steel Alloys
Steel alloys are another material used in piston manufacturing, especially in heavy-duty engines. Steel pistons offer superior strength and thermal conductivity, making them suitable for extreme operating conditions. However, they are heavier than aluminum pistons.
4. Ceramic Composite Materials
In recent years, ceramic composite materials have gained popularity in piston manufacturing due to their exceptional heat resistance and lightweight properties. These materials help enhance engine efficiency and performance by reducing friction and heat generation.
Factors Influencing Piston Material Selection
When designing pistons for specific engine applications, engineers consider various factors that influence the choice of materials. These factors include:
1. Operating Conditions
The temperature, pressure, and speed at which an engine operates play a significant role in determining the suitable material for pistons. Materials with high heat resistance and thermal conductivity are preferred for engines operating under extreme conditions.
2. Weight and Performance
The weight of the piston affects engine performance and fuel efficiency. Lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys are preferred for high-performance engines to reduce inertia and improve engine responsiveness.
3. Cost and Manufacturing Process
The cost of materials and the complexity of the manufacturing process also influence the choice of piston materials. Engineers strive to strike a balance between performance requirements and cost-effectiveness when selecting materials for pistons.
The Future of Piston Materials
As automotive technology continues to advance, researchers are exploring new materials and manufacturing processes to further enhance the performance and efficiency of pistons. From nanostructured alloys to advanced ceramic composites, the future of piston materials holds exciting possibilities for the automotive industry.
In conclusion, pistons are made of a variety of materials, each offering unique properties and advantages. The choice of materials plays a crucial role in determining the performance, efficiency, and durability of an engine. By understanding the different materials used in piston manufacturing, we can appreciate the engineering innovations that drive the automotive industry forward.
HOW ENGINE PISTONS ARE MADE
Frequently Asked Questions
What materials are commonly used to make pistons?
Pistons are typically made from materials like aluminum alloy, cast iron, or steel. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and heat resistance properties, which are crucial for the piston’s function within an engine.
How does the choice of materials affect the performance of pistons?
The materials used in pistons directly impact their performance. Aluminum alloy pistons are lightweight and offer good thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-performance engines. On the other hand, cast iron and steel pistons are heavier but provide greater strength and durability, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Are there any specialized coatings used on pistons?
Yes, pistons may be coated with materials like graphite, molybdenum, or ceramics to improve wear resistance, reduce friction, and enhance overall performance. These coatings help extend the lifespan of the piston and improve its efficiency in the engine.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, pistons are a crucial component of an engine, made primarily of aluminum alloy due to its lightweight and excellent heat dissipation properties. The material composition is essential for ensuring the piston’s durability and longevity under high-stress conditions. Understanding what pistons are made of is fundamental to appreciating their role in the proper functioning of an engine.